
We decided to offer a way more efficient than radiography and less costly than MRI to avoid unnecessary casting and high costs. Currently, we have a gold standard for definitive diagnosis of scaphoid fractures with the normal radiography of MRI with a sensitivity of 91% to 99% (average 96%) and a specificity of 96% to 100% (average 99%) ( 7, 19).Īlthough MRI has an acceptable sensitivity and specificity to detect a hidden scaphoid fracture with normal radiography, given the high cost of the procedure, the need for lower-cost alternatives for the early detection of this type of fracture is felt. Results from several studies have shown that only 5 to 10 percent of patients with suspected fractures with negative radiography have been reported real fractures after casting and further radiography, causing unnecessary downtimes and medical expenses (casting and re-graphs) imposed to the patient ( 15, 19). According to current issues, immobilization with casting is usually done for a disease with clinically suspected fracture, even if there is no visible sign on radiography. Numerous studies have reported the sensitivity of plain radiography after injury 59 to 79% ( 13, 14).
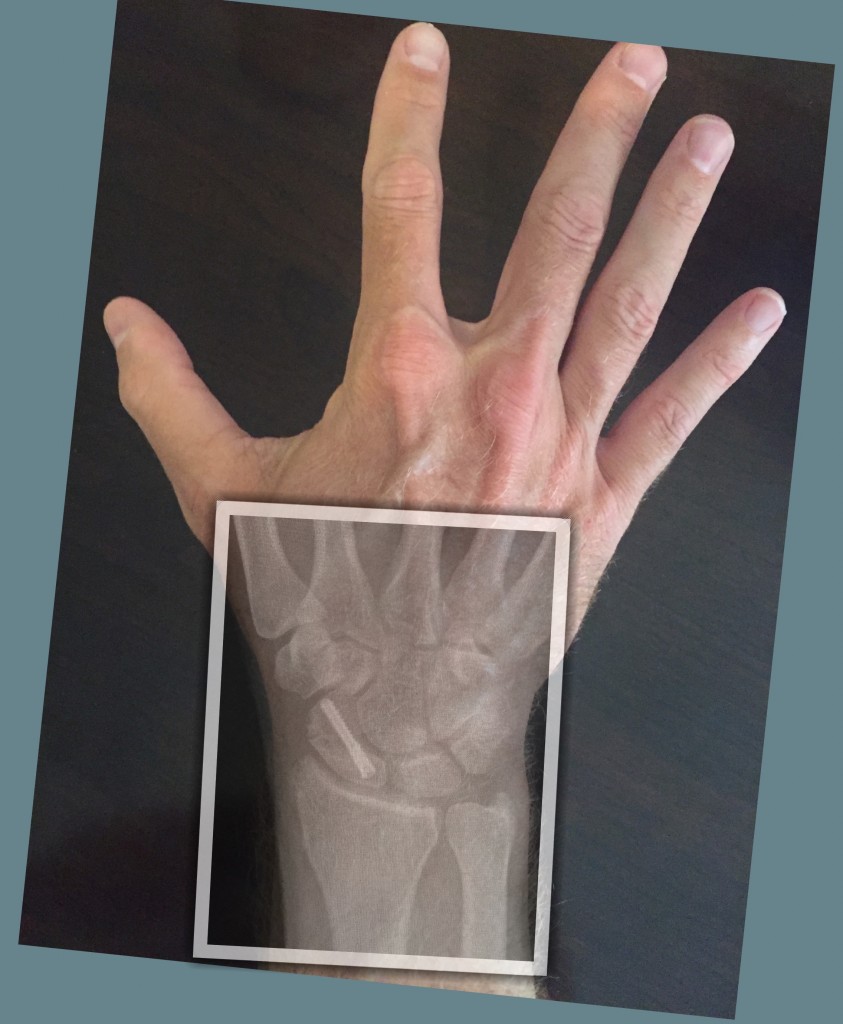
Additionally, this type of fracture is likely not to be detected in the early post-injury radiographs ( 2, 7). Lucentness of fracture site may be hidden and there may only be some changes, such as fading or moving the scaphoid distal fat. This fracture is difficult to be detected with standard radiography and radiography with special scaphoid views should be requested ( 7). Radiographic evaluation of scaphoid fractures includes standard radiography and special scaphoid view ( 2).
In any case, however, the physical examinations possess high sensitivity in the detection of this fracture, its specificity is relatively low (74 to 80%) ( 7). While examining the anatomical snuffbox tenderness, there is a tenderness that is the classic diagnostic finding for this fracture.Īdditionally, inflation and filling anatomical snuffbox may also exist. Taking notes as trauma after falling over, with weight pressure on the wrist in the state of wrist dorsiflexion, can be helpful in diagnosis ( 2, 7). Totally, avascular necrosis occurs in 13 to 40% of cases and scaphoid fracture nonunion in 5 to 12% ( 7). Among the effects of this type of fracture, avascular necrosis of scaphoid bone and nonunion of the proximal part of the scaphoid are more common ( 1, 3, 6, 7, 9, 12). The important point about scaphoid bone is it that it has retrograde blood supply. The most common type is wrist fracture that includes 70 to 80% of scaphoid fractures ( 7). The most common reason for the fracture is to fall onto an outstretched hand, while the wrist has dorsiflexion or a direct axial pressure is applied in line with thumb metacarpal ( 2, 7).Īccording to the fracture site, scaphoid fractures can be divided into three groups: Tuberosity and Distal Pole Fractures, Wrist Fractures and Proximal Pole Fractures. This fracture occurs in young adults between 15 and 30 years old and is rare in patients with immature skeletal system, because wrist is completely cartilaginous at birth and its structure remains nearly completely cartilaginous until late childhood and adolescence ( 7). Scaphoid fracture is the most common fracture among the bones of the wrist ( 1- 11), so that it includes 62 to 87 percent of wrist fractures.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
